How To Make Constrcut With Template In C++
A template is a simple and yet very powerful tool in C++. The simple thought is to pass data blazon every bit a parameter so that we don't demand to write the same code for different information types. For case, a software visitor may need sort() for unlike information types. Rather than writing and maintaining the multiple codes, nosotros can write one sort() and laissez passer data blazon as a parameter.
C++ adds two new keywords to support templates: 'template' and 'typename'. The second keyword tin always exist replaced by keyword 'class'.
How exercise templates work?
Templates are expanded at compiler time. This is similar macros. The difference is, the compiler does type checking before template expansion. The idea is simple, source code contains only office/grade, merely compiled code may contain multiple copies of same function/class.
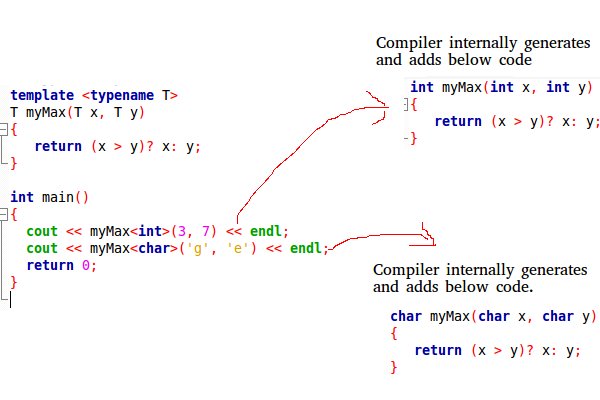
Office Templates Nosotros write a generic part that tin be used for different information types. Examples of part templates are sort(), max(), min(), printArray().
Know more on Generics in C++
CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template < typename T>
T myMax(T x, T y)
{
return (ten > y)? x: y;
}
int main()
{
cout << myMax< int >(iii, 7) << endl;
cout << myMax< double >(3.0, seven.0) << endl;
cout << myMax< char >( 'g' , 'e' ) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
vii vii g
Below is the program to implement Chimera Sort using templates in C++:
CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template < class T>
void bubbleSort(T a[], int n) {
for ( int i = 0; i < northward - one; i++)
for ( int j = north - 1; i < j; j--)
if (a[j] < a[j - i])
bandy(a[j], a[j - 1]);
}
int chief() {
int a[5] = {10, 50, thirty, 40, 20};
int north = sizeof (a) / sizeof (a[0]);
bubbleSort< int >(a, north);
cout << " Sorted array : " ;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " " ;
cout << endl;
render 0;
}
Output
Sorted array : 10 20 30 40 50
Output:
Sorted array : 10 20 30 40 fifty
Form Templates Like function templates, form templates are useful when a class defines something that is independent of the data type. Can be useful for classes like LinkedList, BinaryTree, Stack, Queue, Assortment, etc.
Following is a simple case of template Array form.
CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template < typename T>
class Assortment {
private :
T *ptr;
int size;
public :
Array(T arr[], int s);
void print();
};
template < typename T>
Assortment<T>::Array(T arr[], int s) {
ptr = new T[s];
size = southward;
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++)
ptr[i] = arr[i];
}
template < typename T>
void Array<T>::impress() {
for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout<< " " <<*(ptr + i);
cout<<endl;
}
int chief() {
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Array< int > a(arr, 5);
a.print();
return 0;
}
Output:
1 ii 3 4 5
Can at that place be more than one arguments to templates?
Yes, like normal parameters, we can pass more than one information types every bit arguments to templates. The following example demonstrates the same.
CPP
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template < class T, class U>
form A {
T ten;
U y;
public :
A() { cout<< "Constructor Called" <<endl; }
};
int master() {
A< char , char > a;
A< int , double > b;
return 0;
}
Output
Constructor Called Constructor Called
Output:
Constructor Chosen Constructor Chosen
Tin we specify default value for template arguments?
Yes, like normal parameters, nosotros can specify default arguments to templates. The following example demonstrates the same.
CPP
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template < class T, class U = char >
class A {
public :
T 10;
U y;
A() { cout<< "Constructor Called" <<endl; }
};
int main() {
A< char > a;
return 0;
}
Output:
Constructor Called
What is the divergence betwixt role overloading and templates?
Both part overloading and templates are examples of polymorphism feature of OOP. Function overloading is used when multiple functions do similar operations, templates are used when multiple functions do identical operations.
What happens when there is a static member in a template course/function?
Each instance of a template contains its own static variable. See Templates and Static variables for more details.
What is template specialization?
Template specialization allows us to accept different code for a particular information blazon. See Template Specialization for more details.
Can we laissez passer nontype parameters to templates?
We can pass non-type arguments to templates. Non-blazon parameters are mainly used for specifying max or min values or any other abiding value for a particular instance of a template. The important thing to note near non-type parameters is, they must be const. The compiler must know the value of not-type parameters at compile fourth dimension. Because the compiler needs to create functions/classes for a specified non-blazon value at compile time. In below program, if we supplant 10000 or 25 with a variable, nosotros get a compiler error. Please see this.
Below is a C++ programme.
CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template < class T, int max>
int arrMin(T arr[], int n)
{
int m = max;
for ( int i = 0; i < north; i++)
if (arr[i] < one thousand)
m = arr[i];
return m;
}
int principal()
{
int arr1[] = {10, 20, fifteen, 12};
int n1 = sizeof (arr1)/ sizeof (arr1[0]);
char arr2[] = {1, 2, 3};
int n2 = sizeof (arr2)/ sizeof (arr2[0]);
cout << arrMin< int , 10000>(arr1, n1) << endl;
cout << arrMin< char , 256>(arr2, n2);
return 0;
}
Output:
ten 1
Here is an example of C++ program to bear witness dissimilar data types using constructor and template. We will perform few deportment
- passing character value by creating an objects in principal() part.
- passing integer value by creating an objects in master() office.
- passing float value by creating an objects in main() part.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
template < class Tl>
grade info
{
public :
info(TI, A)
{
cout<< "\northward" << "A = " <<A<< " size of data in bytes:" << sizeof (ch);
}
};
int main()
{
clrscr();
info< char >p( 'x' );
info< int >q(22);
info< float >r(ii.25);
return 0;
}
Output:
A = x size of data in bytes: ane A = 22 size of data in bytes: 2 A = 2.25 size of data in bytes: four
What is template metaprogramming?
Meet Template Metaprogramming
You may too similar to take a quiz on templates.
Java besides supports these features. Java calls information technology generics .
Please write comments if yous notice anything incorrect, or yous want to share more than information about the topic discussed above.
How To Make Constrcut With Template In C++,
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/templates-cpp/
Posted by: wittethareck.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Make Constrcut With Template In C++"
Post a Comment